Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that can cause serious infections in newborn babies, including sepsis, meningitis, and pneumonia. GBS is commonly found in the vagina and rectum of healthy women, and it can be passed to the baby during delivery. However, with proper screening and treatment, the risk of GBS infection can be significantly reduced. One crucial step in preventing neonatal GBS infections is the collection of GBS specimens during pregnancy.
GBS screening is recommended for all pregnant women between 35 and 37 weeks of gestation. During this screening, a healthcare provider collects samples from the vagina and rectum using a cervical swab. The samples are then sent to a laboratory for analysis. If GBS is detected, the woman will receive antibiotics during labor to reduce the risk of transmitting the bacteria to the baby.
Specimens Collection
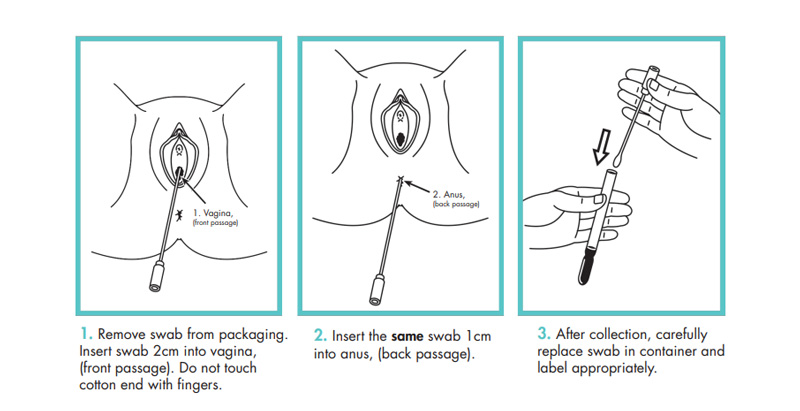
GBS specimens collection is a simple and painless procedure that can have a significant impact on the health of both the mother and the baby. By identifying GBS carriers and providing appropriate treatment, healthcare providers can prevent up to 80% of GBS infections in newborns.
It is essential to note that GBS screening is not a one-time test. Women who test negative for GBS during their first pregnancy may still be carriers in subsequent pregnancies. Therefore, GBS screening should be repeated during each pregnancy.
In addition to GBS screening, pregnant women can take other steps to reduce the risk of GBS infection in their babies. These include:
- Avoiding sexual activity during the last weeks of pregnancy
- Practicing good hygiene, including washing hands frequently
- Seeking medical attention promptly if they experience symptoms of infection, such as fever, chills, or vaginal discharge
GBS specimens collection is a critical component in preventing neonatal GBS infections. Pregnant women should undergo GBS screening between 35 and 37 weeks of gestation, and the procedure should be repeated during each pregnancy. By identifying GBS carriers and providing appropriate treatment, healthcare providers can significantly reduce the risk of GBS infection in newborns.
Potassium Fulvic Acid For Plants,Mineral Sources Fulvic Acid Potassium Fertilizer,Organic Fertilizer Potassium Fulvic Acid,Potassium Fulvic Acid For Agriculture
Zhengzhou Bridge Biochem Co.,Ltd. , https://www.biochemfeeds.com