Epigenetic function of the unique histone component H1foo in mammalian oocytes
First, the research background
Most mammalian histones are bound in a sequence-specific manner to the connecting sequence of DNA, nucleosomes junction will thus produce a highly ordered structure of chromatin gene expression to accurately adjusted. H1foo is a member of the histone H1 family that is specifically expressed in egg cells and is expressed throughout the development of meiotic blastocyst stage oocytes to late two-cell embryos. Moreover, its expression is essential for the maturation of mouse oocytes, and plays an important role in the development of oocytes to fertilized eggs. H1foo has very low sequence homology with other members of the histone H1 family, and its function is poorly understood.
Second, the experimental method
Researchers at the University of Tokyo used a rotary-type laser confocal live cell workstation (CV1000, Yokogawa, Japan) to observe the H1foo embryonic stem cell line (H1foo-ES) that was fused to express GFP protein after construction, and four for experimental control. The cell lines were EGFP-ES, H1s-ES, H1e-ES, H1f0-ES, respectively, which expressed GFP, histone subtypes H1s, H1e, H1f0 and GFP fusion proteins, respectively.
Third, the experimental results
The construction and identification are as follows:

From the experimental results (A), we can see that the GFP of each cell line is distributed in the nucleus and there is no aggregation in the nucleolus; and the GFP expression level of each cell line is the lowest (H), these exogenous groups Protein and styling expression also did not affect changes in endogenous histone expression (B), and endogenous histone mRNA (C) and individual embryonic stem cell marker genes in these embryonic cell lines were also unaffected. (D)
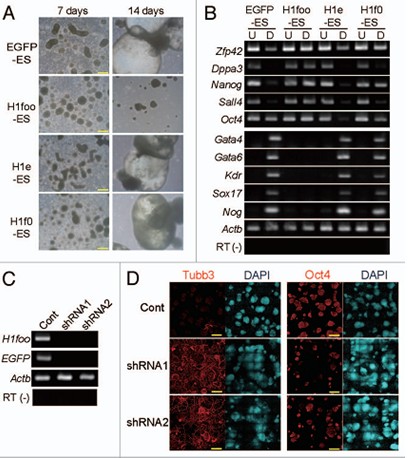
In the next experimental design, the researchers found that the expression of H1foo affects the normal differentiation of embryonic stem cells, phase contrast micrographs. (A) indicates that the cell line expressing the foreign aid H1foo formed a sharp contrast with the development of other control groups after 14 days of culture--developmental delay. Then, RT-PCR was used to detect the transcription of the marker genes in each cell line (U column in B), which can help us locate the developmental stage of the embryo 7 days later (B column B). The detected genes are pluripotent. Stem cell marker genes (Zfp42, Dppa3, Nanog, Sall4 and Oct4); endoderm marker genes (Gata4, Gata6 and Sox17); mesodermal marker gene (Kdr); ectoderm marker gene (Nog). The experimental results were consistent with the microscopic results. The H1foo-ES cell line showed more molecular markers of pluripotent stem cells than the control group, indicating that the expression of H1foo affects the differentiation of ES cells. So if we use exogenous short hairpin RNA (shRNA) to interfere with the transcription of H1foo in cells, will this rescue stagnation be saved? A set of visualized immunofluorescence images (completed by YOKOGAWA's CV1000 confocal system) allowed us to further validate this hypothesis: we induced the shRNA-derived H1foo-ES cell line to differentiate into neural cells, 10 days later, The expression of the neuronal marker molecule TubbIII was up-regulated in the cell line, while the marker molecule of the pluripotent stem cell was significantly decreased.
Fourth, the conclusion of the experiment
From this we can easily conclude that the abnormal expression of H1foo affects the differentiation potential of ES cells.
It has been reported that the H1foo gene is regulated by tissue-specific DNA methylation and methylation-differentiated regions (T-DMR), and in differentiated cells, H1foo expression is also strictly regulated by T-DMR DNA. The inhibition of the base. Cell differentiation also alters epigenetic features within the genome, including methylation and demethylation in the T-DMR region. So is the above role of H1foo already related to methylation?
COBRA methylation analysis experiments confirmed that the methylation of the H1foo-ES group did show resistance in the test after 7 days compared with the above control group, which also indicates that the stagnation of differentiation is also accompanied by stem cells to differentiated state. The methylation shift was blocked (results not shown). Moreover, the results of ChIP experiments also revealed that H1foo is associated with both hypermethylation and hypomethylation sites in the T-DMR region, but some highly methylated regions do not have H1foo binding, so we can only temporarily The regions that are named for these H1foo preferences are H1foo targeting regions, others are non-targeting regions.
Further research was even more surprising. In the H1foo-targeted region, the nuclease sensitivity of low-methylation was higher than that of the control GFP-ES, indicating that these regions have an intimate structure. At the same time, ribozyme-sensitive hypermethylated regions in GFP-ES cells developed resistance in the H1foo-ES cell line. Those areas that are not H1foo bound are resistant to ribozyme digestion. What does this show? ---H1foo is involved in the site-specific localization of nucleosomes, thus leading to changes in methylation.
The answer is finally the truth. This experimental design involves many molecular biology methods, such as RT-PCR, ChIP, COBRA, and the only laser confocal fluorescence imaging image has become a visual highlight in the whole article. The YOKOGAWA CV1000 series mentioned in the article is also a model of the carousel confocal that the company just launched in 2010. It entered the Chinese market in 2011. It is not only compatible with fixed cell sections, but also for long-term observation of living cells and long-term observation. Slice culture is one of the indispensable instrument tools in the laboratory.
Greenhouse Hardware
Greenhouse Hardwares
Greenhouse Cross Connectors are used to tie together two piece of pipe in the greenhouse structure or other application.
Hoop Size: 1-3/8", 1-5/8", 2" [1-7/8" O.D], 2-1/2" [2-3/8" O.D.] Purlin Size: 1 3/8", 1-5/8"
Material: Aluminum Alloy Or Galvanized Steel
Each set includes two Clamps with two Bolts and Nuts
Be used for: Purlin to rafter connections. Trellis system for grapes and other vines. Shade and wind barrier frames.
Cross Connects - Purlin Clamps for Greenhouse
Pipe Connectors Tube Brackets Meta
Greenhouse Cross Connectors (purlin brackets) can be used to connect ridge poles or
purlins to bows. These steel greenhouse connectors are ideally sized for 1
5/8" top rail fence piping.

Greenhouse Hardware,Greenhouses Purlin Bracket,Greenhouse Cross Connectors,Greenhouse Aluminum Purlin Clamp
Ningbo Yokelink Machinery Co.,Limited , https://www.yokelink.com


