Corn seedlings typically exhibit a dark green color, but under improper management—such as insufficient fertilization or adverse weather conditions—their color may change to yellow, red, white, purple, light green, or other abnormal shades. These changes are commonly referred to as yellowing, whitening, purple leaf, stiff leaf, or yellow-green seedlings. Such discoloration not only hinders the normal growth of corn but also reduces yield and quality. Therefore, it's essential to manage these issues effectively.
Yellow leaf seedlings usually start with a light green color and gradually turn yellow, eventually leading to leaf death. This condition can cause empty stalks or barren ears. The causes include poor seed quality, deep sowing that weakens emergence, high planting density that limits nutrient availability, and soil lacking in nutrients. To control this, first, select high-quality seeds with over 98% purity and 90% germination rate. Second, use seed coating or fertilizer soaking before planting. Third, thin out weak, diseased, or overcrowded seedlings when they have 3-4 leaves. Fourth, apply nitrogen fertilizer after seedling emergence to promote growth. Lastly, break up dry clods before and after emergence to ensure proper soil aeration.
White seedlings show white stripes on their leaves, and severe cases result in complete whitening, wilting, and plant death. This is often due to zinc deficiency in the soil. Control methods include applying zinc fertilizer as a base fertilizer (1.5–2.0 kg per 667 square meters), using zinc-coated seeds, or foliar spraying with a solution of 0.2–0.3 kg zinc sulfate per 100 kg of water, applied 2–3 times every 7 days.
Purple seedlings appear when the leaves and leaf sheaths turn from green to red and then to purple, typically around the 3-leaf stage. They are caused by phosphorus deficiency, reduced root absorption, and impaired chlorophyll synthesis, especially under low temperatures. This leads to stunted growth, weak stems, and even plant death. To address this, increase the use of phosphate fertilizer as a base (40–50 kg per 667 square meters) and spray potassium dihydrogen phosphate at 0.2% concentration, 2–3 times with an 8-day interval.
Stiff leaf seedlings occur before the third leaf stage, with small, pale green leaves, weak growth, and black roots. After transplanting, new leaves may be green, but older ones become yellow and rigid. This is often due to excessive chemical fertilizers, poor seed-fertilizer separation, drought, or poor soil conditions. Control measures include using well-decomposed organic fertilizer, maintaining proper moisture and temperature, practicing timely irrigation, weeding, and applying foliar fertilizers when needed.
Yellow-green seedlings are characterized by thin, narrow leaves with yellow-green stripes, which can progress to dark brown and eventual death. This condition often starts from the lower leaves and moves upward, increasing the risk of lodging. To prevent this, increase potassium fertilizer application based on soil analysis, or supplement with wood ash if potassium is lacking. For severe cases, apply potassium dihydrogen phosphate and ash leaching solution at the 3-leaf stage to restore health.
Micro Laser Distance Sensor
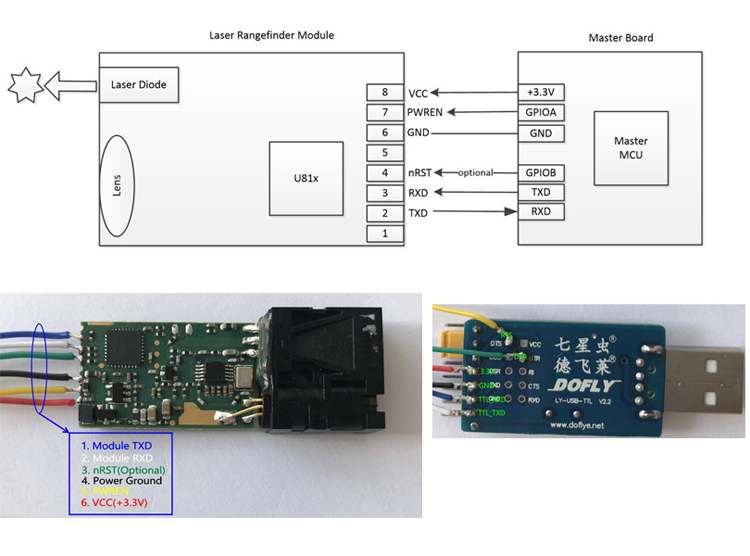
New product of U85 micro laser distance sensors use highly focused class 2 laser to detect objects or measure distances, and can return a measured value via varieties intface( serial, usb, rs232, rs485, bluetooth etc.). The electronic distance sensor is a very small Laser Distance Sensor, but high resolution up to 1mm and long distance measuring sensor - teachable measuring range of up to 30m. Extremely accurate distance sensing sensors, errors down to ± 1mm. And the mini sensors and measurements support continuous measurement function, great for compact solutions(eg: robots) with the smallest Laser Distance Sensor of the world!
Parameters of U85:
|
Accuracy
|
±1 mm (0.04 inch)
|
|
Measuring Unit
|
mm
|
|
Measuring Range (without Reflection)
|
0.03-20m/0.03-30m
|
|
Measuring Time
|
0.1~3 seconds
|
|
Laser Class
|
Class II
|
|
Laser Type
|
620nm-690nm, <1mW
|
|
Size
|
41*17*7mm (±1 mm)
|
|
Weight
|
About 4g
|
|
Voltage
|
DC2.0~3V
|
|
Electrical Level
|
TTL/CMOS
|
|
Certifications
|
CTNT, FDA, CE, FCC, RoHS, etc.
|
|
Operating Temperature
|
0-40 ℃ (32-104 ℉ )
|
|
Storage Temperature
|
-25~60 ℃ (-13~140 ℉)
|
Mini Laser Distance Sensor,Optical Laser Distance Sensor,Smallest Laser Range Sonsor,Laser Measuring Sensor
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jrt-measure.com
